|
Trends
Logic in DB
Drivers
ODBC
JDBC
OLE DB
.NET
Podcast
SQL:2003
MS SQL 2005
Webcast
SQL:2003
MS SQL 2005
|
|
<< Prev 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Next >>
Restructure Example
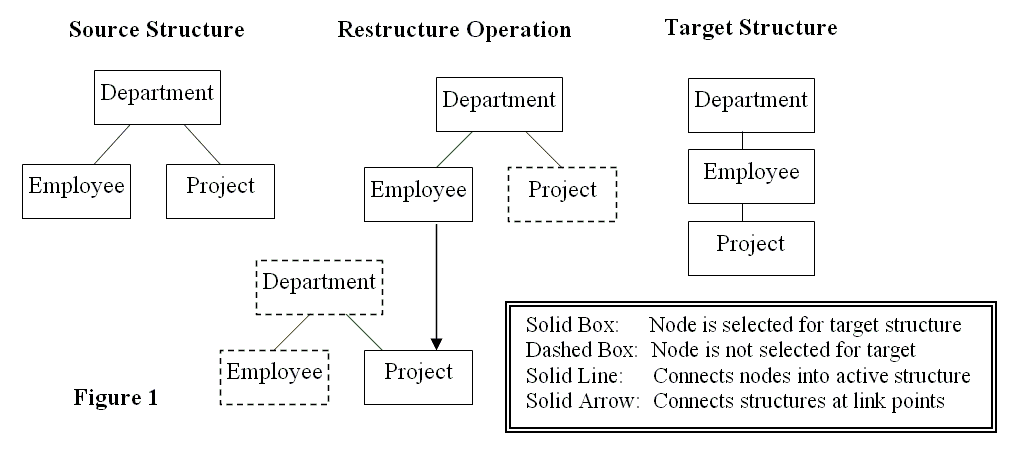
Lets use the hierarchical source structure composed of Department, Employee, and Project nodes shown below in Figure 1 in an example of a Restructuring operation. If the Project node contains a project manager Employee foreign key, then the Project node can be rejoined under the Employee node using this relationship. The semantics for the target structure are that the projects are placed under their correct employee manager. Restructuring can involve taking the structure apart and rejoining it differently as shown in Figure 1 below under the Restructure Operation heading. One way to do this physically or logically is to use duplicate copies of the data structure also shown below. The legend box below describes the meaning of the structure diagrams used in this article.
Enlarge
|
 Fast, reliable data access for ODBC, JDBC, ADO.NET and XML Fast, reliable data access for ODBC, JDBC, ADO.NET and XML
|
In the example in Figure 1 and in most other examples using this technique, you will notice that the lower level structure copy under the Restructure or Reshaping Operation heading is being linked to or synchronized to a point below its root in the structure copies. In the example of Figure 1, it is the lower level structure Project node located below the root. This is OK because the Project node in the lower level is still under the influence of its data ancestry which in this structure is the Department node. In the case of fixed contiguous structures like XML, the Project node occurrences are already in place. In the case of logical structures like relational, the structure has been defined in a view which is materialized before being accessed which builds the correct meaningful Project node data occurrences. This enables linking or referencing below the root of the lower level structure.
|
<< Prev 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Next >>
Database Server Watch SQL Summit Home Page Articles

© 2007, Ken North Computing LLC, All rights reserved.
|
|

|